The Untold Story of Collagen Supplements
- Dec 1, 2025
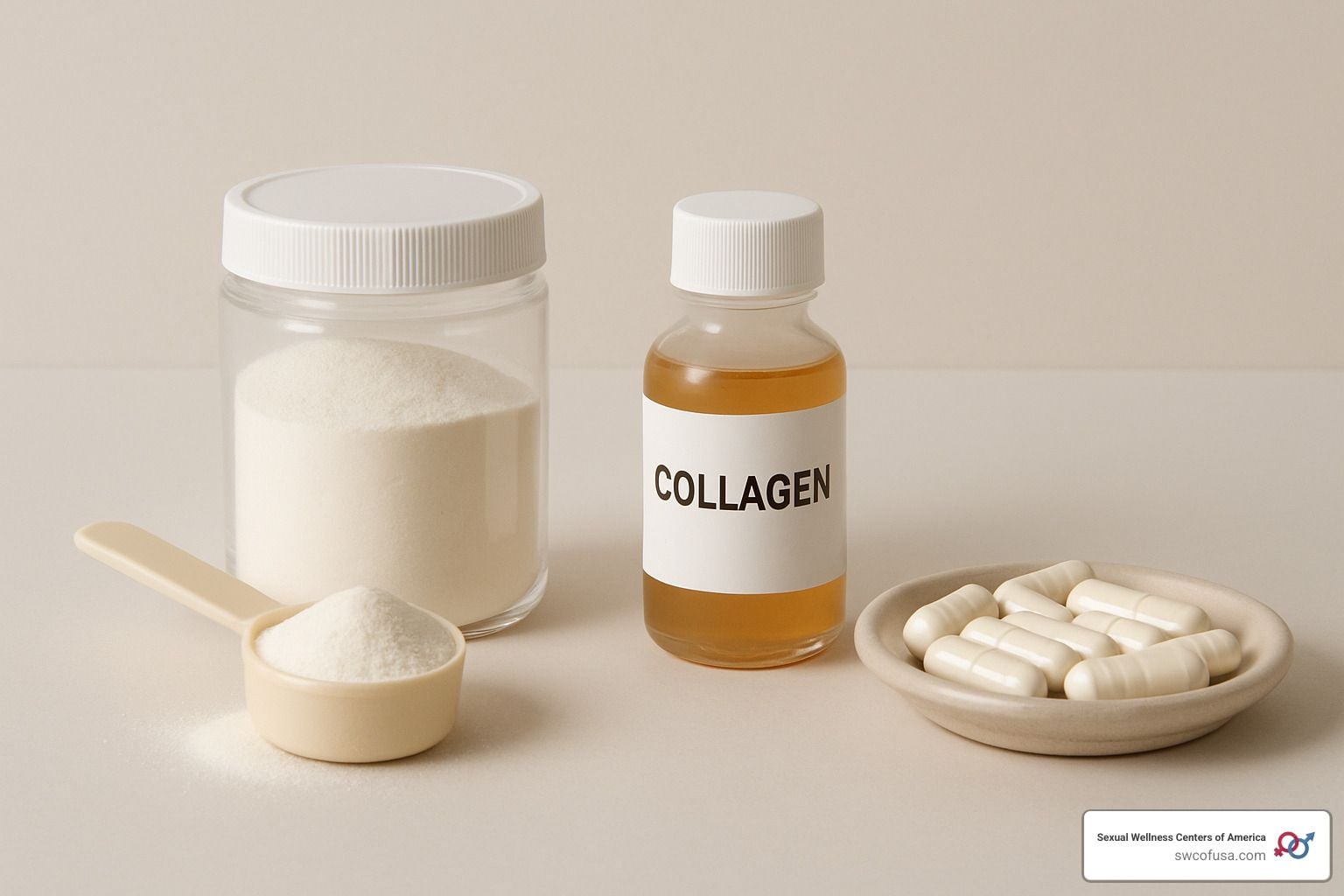
Collagen is a powerhouse protein, essential for maintaining strong bones, promoting firm skin, and assisting in wound healing. Despite the body’s ability to produce collagen naturally, this capacity diminishes as we age, leading some people to turn to supplements. They are generally safe to use, though some people may experience rare side effects.
Minor stomach upset ranks as the most frequently seen side effect of collagen supplements, with some users reporting digestive complications. Collagen is commercially available in liquid and powder form, though current research does not suggest one form is more prone to cause side effects than the other.
Regulation of supplements is currently not handled by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which means safety and effectiveness are not guaranteed. If you find yourself experiencing digestive distress after starting a collagen supplement, the advice is to quit the supplement and discuss the situation with your healthcare provider.
Allergic responses are a possibility with any medication or supplement, and collagen is no exception. Hypersensitivity reactions may appear as a red rash and itchiness. Other potential allergy symptoms could include responses studied in case studies related to individuals exposed to bovine collagen, which are supplements derived from the connective tissues of cows.
In rare cases, collagen supplements can spark a serious reaction. One documented case discusses an individual developing Stevens-Johnson syndrome after using a collagen supplement. This extreme reaction caused painful blisters, skin shedding, fever, flu-like symptoms, and possible organ damage.
Healing the misunderstanding that every type of collagen supplement shares the same risk, the study pinned this severe reaction on a fish-derived, or marine, collagen. Experts suggest that collagen from this source may be more likely to catalyze hypersensitivity reactions.
At a broader spectrum, research views the risk of side effects from taking a collagen supplement as very low and generally safe. The study authors agree that even taking high doses is unlikely to catalyze adverse effects or reactions. Exceptions are out there, as most people do not necessarily need to take a collagen supplement. The body can naturally produce its own collagen, fueled by the protein in our diets.
To boost this natural evolution, protein-packed foods can come into play, such as lean meats, dairy, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and whole grains. Your diet also needs other key nutrients to enhance collagen production, including vitamin C, copper, and proline.
Studies confirm that maintaining a balanced diet rich in protein and vitamins can support normal collagen production. After the age of 40, your body slows collagen production, decreasing approximately by about 1% per year. If you're considering starting a collagen supplement, it's recommended to consult with your healthcare provider first.
The majority of healthy adults are likely to safely consume a daily collagen supplement without adverse effects. Exceptions exist for those who have had a history of controversial reactions to collagen supplements, which typically get sourced from the connective tissues of cows, pigs, or fish. It's advised against taking a collagen supplement if you are pregnant, nursing, or are taking certain medications. Particularly, collagen supplements that contain high doses of biotin may interfere with thyroid medications.